The Evaporative Emission Control System (EVAP) is designed to minimize pollution and improve fuel efficiency in vehicles. Despite its importance, many people are unaware of what it does, how it works, or the potential issues it can face. When the EVAP system malfunctions, it can lead to increased emissions, reduced engine performance, and other problems.
What is the EVAP System?
Its primary purpose is to capture and control fuel vapors that escape from the fuel tank and fuel system. When gasoline evaporates, it releases harmful vapors into the air.
These vapors contribute to air pollution and can be dangerous if inhaled. The EVAP system prevents these vapors from reaching the atmosphere by capturing them and storing them in a canister filled with activated charcoal.
When the engine runs, the system routes the trapped vapors back into the engine to be burned off. This process not only helps reduce pollution but also improves fuel efficiency, making cars more environmentally friendly.
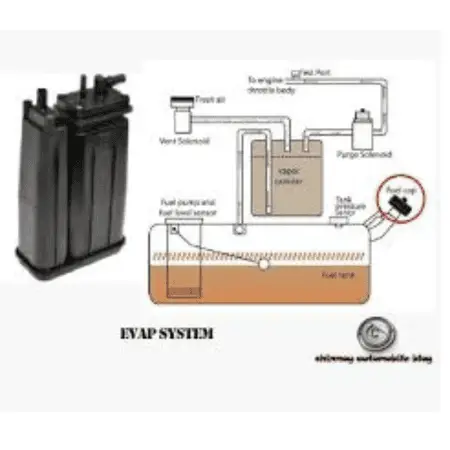
Components of the EVAP System
The EVAP system consists of several key components that work together to manage and control fuel vapors:
Fuel Tank: The fuel tank stores gasoline and is the source of fuel vapors. It has valves and hoses connected to other parts of the EVAP system to channel the vapors.
Charcoal Canister: This canister is filled with activated charcoal, which absorbs and stores fuel vapors. The charcoal canister prevents these vapors from escaping into the atmosphere.
Purge Valve: The purge valve controls the flow of fuel vapors from the charcoal canister to the engine. It opens at specific times, usually when the engine is running, to allow vapors to be drawn into the engine and burned.
Vent Valve: The vent valve allows fresh air to enter the charcoal canister. This helps to purge the canister of fuel vapors, ensuring it can continue to absorb more vapors from the fuel tank.
Fuel Cap: The fuel cap seals the fuel tank and prevents vapors from escaping directly into the air. A faulty or loose fuel cap can cause the EVAP system to malfunction, leading to increased emissions.
Hoses and Tubes: Various hoses and tubes connect the components of the EVAP system. These ensure the proper flow and control of fuel vapors throughout the system.
Each of these components plays a vital role in the functioning of the EVAP system. Together, they help to capture, store, and eventually eliminate harmful fuel vapors, making cars cleaner and more efficient.

EVAP Leak Codes
When an EVAP leak occurs, the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics (OBD-II) system generates specific trouble codes. These codes help identify issues within the evaporative emission control system. Understanding these common EVAP codes can aid in diagnosing and fixing the problem.
P0440 – Evaporative Emission Control System Malfunction: This code indicates a general fault in the EVAP system. It means the system is not functioning correctly, but it does not specify the exact component that is malfunctioning. Potential causes include a loose gas cap, a cracked hose, or a defective valve.
P0441 – Evaporative Emission Control System Incorrect Purge Flow: This code signifies that the purge valve is not operating properly. The valve might be stuck open or closed, causing an incorrect flow of fuel vapors from the charcoal canister to the engine. Common causes include a faulty purge valve or clogged lines.
P0442 – Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak): This code indicates a small leak in the EVAP system. The system has detected a minor escape of fuel vapors, often due to a loose gas cap, a small crack in a hose, or a slight defect in the charcoal canister.
P0445 – Evaporative Emission Control System Purge Control Valve Circuit Shorted: This code means that there is an electrical issue with the purge control valve circuit. It could be due to damaged wiring or a short circuit, preventing the valve from functioning correctly.
P0455 – Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Large Leak): This code signals a significant leak in the EVAP system. A large amount of fuel vapor is escaping, which could be caused by a severely damaged hose, a broken charcoal canister, or a loose gas cap.
P0456 – Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Very Small Leak): This code indicates a very small leak in the system. It suggests a minor escape of vapors, potentially due to a slightly loose gas cap, a small crack in a hose, or a minor defect in a component.
P0466 – Evaporative Emission Control System Vent Control Circuit Malfunction: This code points to an issue with the vent control circuit. It could be due to a malfunctioning vent valve, damaged wiring, or a short circuit, preventing the proper purging of fuel vapors.
P0457 – Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Fuel Cap Loose/Off): This code specifically indicates that the fuel cap is either loose or missing. The EVAP system has detected an immediate escape of fuel vapors due to an improperly sealed fuel tank.
By understanding these common EVAP codes, vehicle owners and mechanics can more accurately diagnose and address issues within the EVAP system. Proper maintenance and timely repairs can ensure the system functions correctly, reducing emissions and improving overall vehicle performance.

How to Fix EVAP System Issues
The EVAP (Evaporative Emission Control) system in your vehicle prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. If there’s an issue, it can lead to increased emissions and reduced fuel efficiency. Follow these steps to diagnose and fix common EVAP system problems.
1. Identify the Symptoms
First, recognize the signs of EVAP system issues:
- Check Engine Light (CEL) is on.
- Fuel odor near the vehicle.
- Decreased fuel efficiency.
- Difficulty starting the car.
2. Scan for Trouble Codes
Use an OBD-II scanner to check for trouble codes related to the EVAP system. Common codes include P0440 (EVAP System Malfunction) and P0442 (EVAP System Leak Detected).
3. Inspect the Gas Cap
A loose or damaged gas cap is a common cause of EVAP issues.
- Tighten the gas cap.
- Inspect for cracks or damage.
- Replace if necessary.
4. Check EVAP Hoses and Lines
Inspect the hoses and lines for any signs of damage or leaks.
- Look for cracks, holes, or disconnections.
- Replace damaged hoses or reconnect loose lines.
5. Test the Purge Valve
The purge valve releases fuel vapors into the engine for combustion. A faulty purge valve can cause EVAP issues.
- Use a multimeter to check for electrical continuity.
- If the valve is stuck open or closed, replace it.
6. Inspect the Charcoal Canister
The charcoal canister stores fuel vapors until they can be burned in the engine.
- Check for signs of physical damage or fuel saturation.
- Replace the canister if it’s clogged or damaged.
7. Perform a Smoke Test
A smoke test can help locate leaks in the EVAP system.
- Use a smoke machine to fill the EVAP system with smoke.
- Observe for smoke escaping from hoses, lines, or components.
- Repair or replace the leaking parts.
8. Clear the Trouble Codes
After making repairs, clear the trouble codes using the OBD-II scanner.
- Disconnect the scanner and start the vehicle.
- Ensure the Check Engine Light stays off and the vehicle runs smoothly.
9. Monitor the System
Keep an eye on the EVAP system after repairs to ensure no new issues arise.
- Regularly check for any new trouble codes.
- Maintain a habit of inspecting the gas cap and EVAP components during routine vehicle maintenance.
By following these steps, you can effectively diagnose and fix common EVAP system issues, ensuring your vehicle runs efficiently and reduces harmful emissions.
Repairing the EVAP System: What It Might Cost You
Fixing the EVAP system can vary in cost depending on the problem. Here’s a breakdown of what you might expect:
- Gas Cap Replacement: If it’s just the gas cap, you’re looking at around $15 to $30.
- Hose or Line Repair: For damaged hoses or lines, it could cost between $50 and $100.
- Purge Valve Replacement: This part usually runs from $50 to $150, depending on your car’s make and model.
- Charcoal Canister Replacement: Replacing the charcoal canister can be more expensive, typically between $200 and $600.
- Smoke Test: If you need a smoke test to find leaks, expect to pay about $70 to $150.
These are general estimates, and actual costs can vary based on your location and vehicle. Checking with a local mechanic will give you a more accurate idea of the cost.
Must Read
- How to Fix a Gear Shift Indicator Light That’s Not Working
- Why Are Tesla Tires So Expensive? 10 Factors
- How To Clean Radar Sensors Dirty – ( Guide )
Conclusion
Understanding what an EVAP leak is and how to deal with it is essential for every car owner. Regular maintenance, timely repairs, and staying informed about your vehicle’s systems can keep you on the road without issues.
